How Does Atomic Radius (Size) Vary On The Periodic Table?
Learning Objectives
- Define atomic radius.
- Describe how the atomic changes within a menstruum.
- Describe how the diminutive radius changes within a group.
How can all of these people fit in such a minor space?
 Events draw large numbers of people to them. Even an outdoor event tin make full so that there is no room for more people. The crowd chapters depends on the corporeality of space in the venue, and the amount of infinite depends on the size of the objects filling it. Nosotros can get more people into a given space than we can elephants, because the elephants are larger than people. We can get more than squirrels into that same space than we can people for the same reason. Knowing the sizes of objects nosotros are dealing with can exist important in deciding how much infinite is needed.
Events draw large numbers of people to them. Even an outdoor event tin make full so that there is no room for more people. The crowd chapters depends on the corporeality of space in the venue, and the amount of infinite depends on the size of the objects filling it. Nosotros can get more people into a given space than we can elephants, because the elephants are larger than people. We can get more than squirrels into that same space than we can people for the same reason. Knowing the sizes of objects nosotros are dealing with can exist important in deciding how much infinite is needed.
The size of atoms is important when trying to explain the behavior of atoms or compounds. One of the ways we tin can express the size of atoms is with the diminutive radius . This data helps us empathize why some molecules fit together and why other molecules accept parts that get too crowded under certain atmospheric condition.
The size of an atom is defined past the edge of its orbital. Still, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact are variable under different conditions. In order to standardize the measurement of atomic radii, the distance betwixt the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together is measured. The atomic radius is divers as one-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together.

Figure 1. The atomic radius (r) of an cantlet can be defined equally i one-half the distance (d) betwixt two nuclei in a diatomic molecule.
Atomic radii have been measured for elements. The units for atomic radii are picometers, equal to 10−12 meters. Every bit an example, the internuclear distance betwixt the ii hydrogen atoms in an H2 molecule is measured to be 74 pm. Therefore, the atomic radius of a hydrogen atom is [latex]\frac{74}{ii}=37\text{ pm}[/latex].
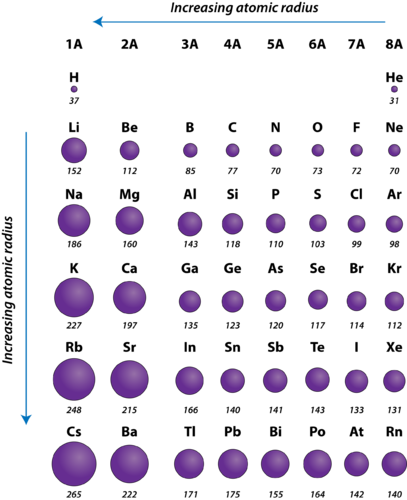
Figure 2. Atomic radii of the representative elements measured in picometers.
Periodic Tendency
The diminutive radius of atoms by and large decreases from left to right across a period. At that place are some small exceptions, such as the oxygen radius being slightly greater than the nitrogen radius. Within a period, protons are added to the nucleus as electrons are being added to the same principal energy level. These electrons are gradually pulled closer to the nucleus because of its increased positive charge. Since the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons increases, the size of the atoms decreases. The effect lessens as ane moves further to the right in a menses because of electron-electron repulsions that would otherwise cause the atom's size to increase.
Group Tendency
The atomic radius of atoms more often than not increases from top to lesser inside a group. As the atomic number increases downward a group, there is again an increment in the positive nuclear accuse. However, there is also an increase in the number of occupied principle free energy levels. College main energy levels consist of orbitals which are larger in size than the orbitals from lower energy levels. The effect of the greater number of chief energy levels outweighs the increase in nuclear charge and so atomic radius increases downwards a grouping.

Figure 3. A graph of diminutive radius plotted versus atomic number. Each successive period is shown in a different color. As the atomic number increases within a menstruum, the atomic radius decreases.
Summary
- Diminutive radius is determined as the altitude between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together.
- The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to correct across a menses.
- The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group.
Practice
Employ the link below to reply the following questions:
http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Inorganic_Chemistry/Descriptive_Chemistry/Periodic_Table_of_the_Elements/Atomic_Radi
- What influences the diminutive size of an atom?
- What is a covalent radius?
- What is an ionic radius?
Review
- Define "atomic radius."
- What are the units for measurement of atomic radius?
- How does the atomic radius change across a menses?
- How does diminutive radius change from top to bottom within a group?
- Explicate why the diminutive radius of hydrogen is then much smaller that the atomic radius for potassium.
Glossary
- diminutive radius: The diminutive radius is defined as i-half the altitude between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together.
How Does Atomic Radius (Size) Vary On The Periodic Table?,
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/cheminter/chapter/periodic-trends-atomic-radius/
Posted by: batemanbillostrand.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Does Atomic Radius (Size) Vary On The Periodic Table?"
Post a Comment